Xahau: CRON
Modern businesses increasingly rely on automation — not just if something happens, but when. On the Xahau network, CRON introduces a native way to schedule actions directly on-ledger, enabling predictable, time-based behavior.
What Is CRON
In traditional computing, “CRON” refers to a scheduler that runs tasks at predefined times (for example, daily billing or weekly reports).
 CRON Automated Time Conditions
CRON Automated Time Conditions
Xahau has adopted this concept, allowing logic to execute automatically based on time rather than user interaction.
How It Works On Xahau
CRON on Xahau is implemented as a first-class ledger feature.
Once a CRON task is registered, the network itself ensures that it executes at the specified interval. This removes reliance on off-chain servers, bots, or third-party automation services — a key requirement for true 'layer one' time-based execution.
Time Instead
Up until CRON was activated, Xahau required an external trigger (user transaction) to execute 'hook' smart contracts attached to each account. It's new CRON system flips this model: actions can occur purely because time has passed.
This is an entire new category of ways to trigger smart contracts.
Technical Stuff
CRON scheduling rules are stored and enforced on-ledger, making them transparent, tamper-resistant, and verifiable by all participants. The development pattern is fairly intuitive: A hook registers a CRON schedule once, the network invokes it at the scheduled time, the hook detects CRON context, executes time-based logic, and optionally re-schedules itself.
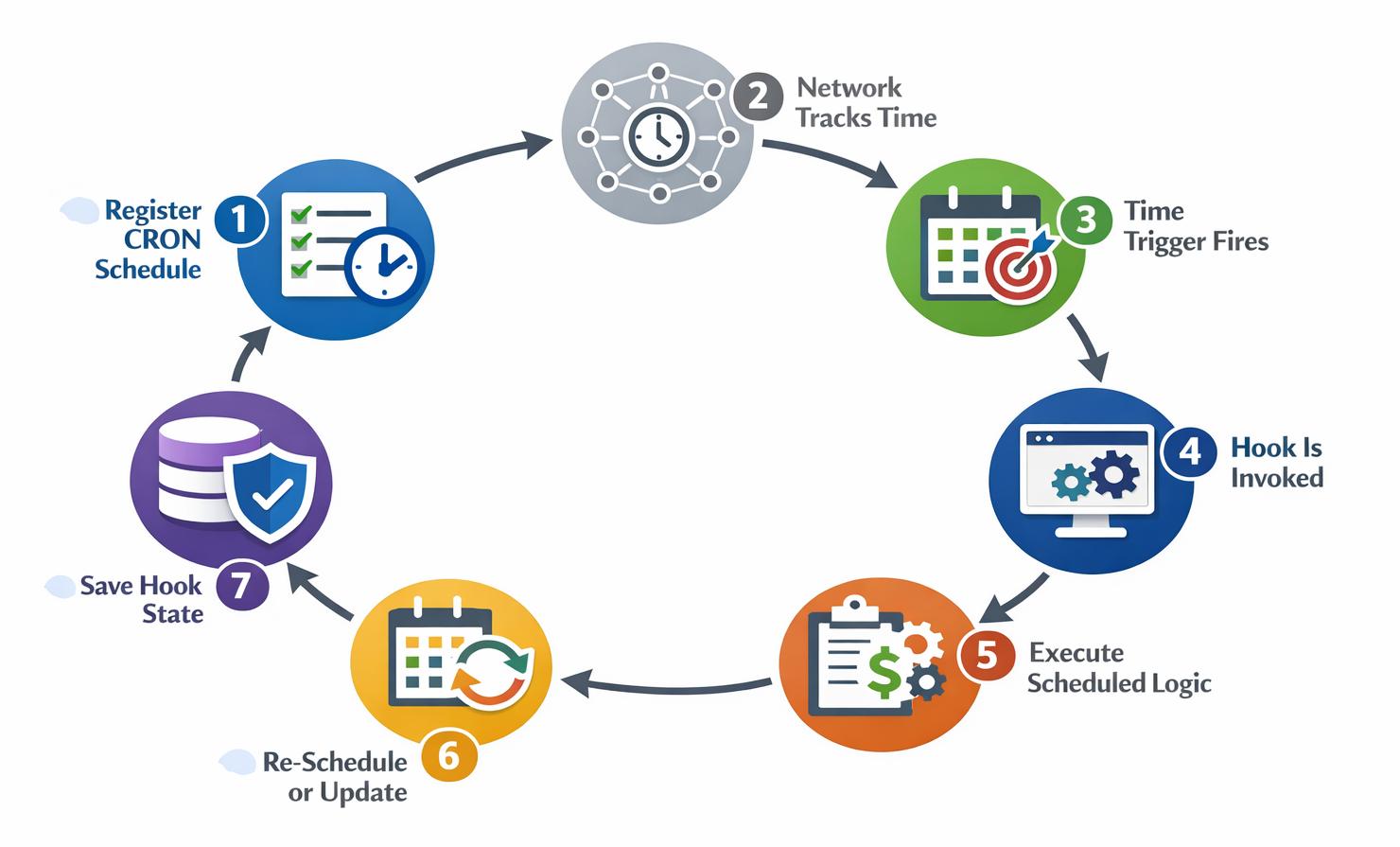 CRON Execution Pattern
CRON Execution Pattern
The official documentation states:
When a cron is ready to execute, the cron engine inserts a pseudo-transaction of type 'cron' into the ledger. This pseudo-transaction contains an owner field referencing the originating hook account. The scheduled hook will be invoked automatically at the specified intervals without requiring external triggers.
Hook developers must enable collect calls (hsfCOLLECT flag) on their hooks, as the owner constitutes a weak transactional stakeholder (TSH) when the cron pseudo-transaction executes.
Current Status Of CRON Amendment
CRON is currently only available on the Xahau testnet.
Ahead of it being enabled on-ledger, a fix was recently proposed and adopted by the validators:
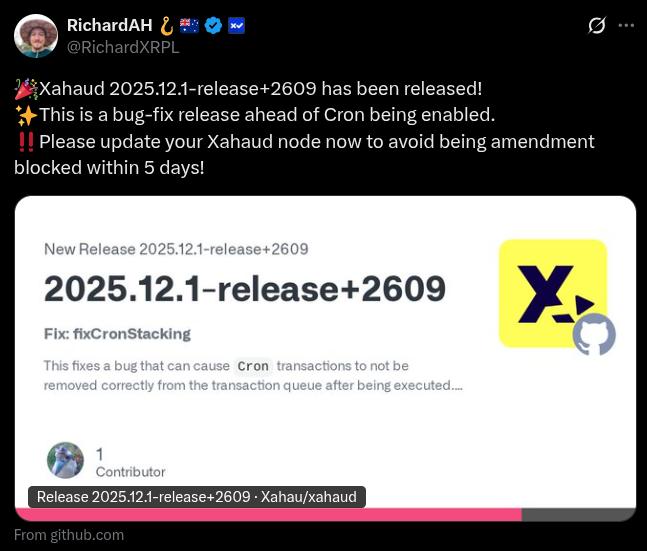 CRON Bug Fix On Xahau
CRON Bug Fix On Xahau
"fixCronStacking" addresses an edge case where multiple CRON-triggered executions could accumulate (stack) and then execute back-to-back in a single ledger, rather than being spread across ledger closes as intended.
A needed fix before go-live.
Use Cases
CRON enables a range of common business scenarios:
- recurring payments
- automated revenue sharing
- time-locked releases of funds
- periodic state updates
- scheduled governance actions (think Evernode)
Because execution is guaranteed by the network, businesses can reduce 'layer two' code and instead move it on-ledger.
This also serves the purpose of reducing risk for a smart contract that may have previously depended on a Web 2.0 overlay; instead of depending on a person or company, stakeholders can rely on code.
True Automation At Layer One
CRON on Xahau represents a move toward time-aware ledger networks that better match real-world business needs.
By enabling scheduled actions without external dependencies, Xahau lowers complexity, improves trust, and opens the door to new classes of decentralized business applications.
X>
Sources:
https://x.com/RichardXRPL/status/1995661845018095633?s=20
https://xahscan.com/amendment/DD6ABC68C1F37392E521EF6FF1475A11576D87C1BC36D9C9E4F0E6C09D18C120
https://xahauexplorer.com/en/amendment/Cron
https://xahau.network/docs/features/amendments/
https://xahau.network/docs/protocol-reference/transactions/transaction-types/cronset/
https://xahau.network/docs/protocol-reference/ledger-data/ledger-objects-types/cron/







